What is Ethereum(ETH) 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0 Introduction
Finance, trade, agriculture, and healthcare have all been disrupted as a result of blockchain technology. Bitcoin was the first widely usedblockchain application, but since then, over 9,000 more cryptocurrencies have emerged. Ethereum is the largest general-purpose blockchain and has the second-highest market capitalization. The goal of Bitcoin is to become a store of wealth and an inflation hedge that is simple and safe to send. Ethereum, on the other hand, was created with smart contracts and Dapps in mind (decentralized apps). Ethereum is fantastic; however, it is far from perfect. The Ethereum Foundation has the ability to improve aspects like performance and security, which it is doing with Ethereum 2.0.

Why ETH 2.0?
Users of the Ethereum network will be pleased because ETH will change its fee structure, resulting in lower transaction fees. This means that current miners will earn less per transaction for the new inclusion fee than for Ethereum's auction-style fee market, but it is expected that their cost per transaction will decrease due to PoS's increased energy efficiency, and the number of transactions will increase as a result of the lower cost benefiting both the user and the Validator.
Due to the general lower prices and faster performance of ETH 2.0, additional sorts of Defi transactions will be available, as well as new and different forms of Security Tokens, NFTs, and other Distributed Finance applications that were not feasible with ETH 1.0.
With zero knowledge rollups and optimistic rollups, ETH 2.0 will enable for more complicated and less expensive smart contracts. Rollups bundle all transaction data and make it available on Ethereum at a lower cost than regular blockchain-based transactions would. Rollups' associated computation load is handled off-chain, resulting in increased throughput and transactional cost-efficiency.
Sharding will democratize the Network, allowing regular people to utilize Ethereum on their personal devices in the future. The blockchain will become even more decentralized as the number of network participants grows. ETH issuance will also be reduced; ETH co-founder Vitalik Buterin has stated that new token issuance under ETH 2.0 should be between 100,000 and 2 million per year, down from the current 4.7 million per year, potentially increasing coin demand.
How is Ethereum 2.0 different from Ethereum 1.0?
Ethereum 2.0, also known as Eth2 or Serenity, is the first upgrade to the Ethereum Classic blockchain, with the goal of improving the Ethereum network's speed, efficiency, and scalability while also improving security and making it more sustainable. Don't worry if you already own ETH; there's nothing you need to do; the ETH 2.0 upgrade is taking place behind the scenes, and holders should never notice the difference.
Bottlenecks have been observed by Eth-1.0 users, and there is still a need to improve the number of potential transactions per second (currently 15 to 45). The following are the two key structural changes in Eth2:
- Proof of stake–This is a consensus mechanism for Validators, who are Ethereum blockchain facilitators who examine ongoing transactions rather than Ethereum Proof of Work miners. Validators are required to post a 32ETH bond in order to avoid fraud.
- Sharding-The process of dividing a blockchain into shards (multiple blockchains.) Sharding increases efficiency by allowing validators to keep track of their own Shard's information. To avoid manipulation and increase security, validators will be swapped across shards, with communication between shards via the Beacon Chain.
The main distinction is the "consensus process" employed (confirming a transaction). Proof of work (PoW) is used in Ethereum, whereas proof of stake will be used in Ethereum 2.0. (PoS). Click here to know more details about the difference.
The Work's Proof In its current form, the PoW mechanism is a computationally and energy-intensive process that involves solving a complex mathematical puzzle that is currently used by Ethereum miners for transaction validation. The miner who solves the riddle the fastest wins a prize. The PoW approach is expected to encourage innovation in the renewable energy sector.
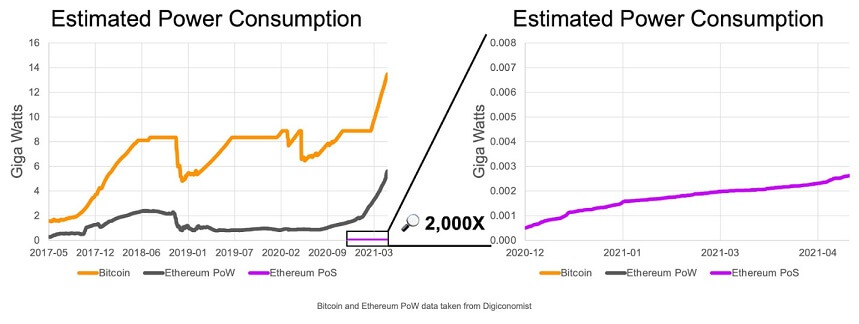
Validators, rather than miners, verify transactions in Proof of Stake. Because securing a blockchain with PoS utilizes far less computational power for block generation, it is more energy efficient than PoW. According to the Ethereum Foundation, ETH 2.0 will use 99.95% less energy than ETH 1.0.
Comments
Post a Comment